Aluminum profiles are essential components in a variety of industries, known for their versatility, strength, and lightweight properties. These extruded shapes are manufactured by pushing aluminum through a shaped die, resulting in a range of profiles that cater to diverse applications. From construction to automotive, the utilization of aluminum profiles has transformed conventional practices, enabling innovative designs and improved functionality.
In the construction industry, aluminum profiles are favored for their resilience and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for window frames, doors, and structural supports. Meanwhile, in the manufacturing sector, these profiles are utilized to create customized machinery frames, conveyor systems, and housing for electronic devices. The adaptability of aluminum profiles allows them to be tailored to specific requirements, thereby enhancing efficiency and performance across different applications.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for lightweight yet durable materials persists. Aluminum profiles stand out as a sustainable solution, contributing to energy efficiency and reduced overall material consumption. In this discussion, we will delve deeper into the various applications of aluminum profiles across multiple sectors, exploring their advantages and the innovations they bring to modern engineering and design.


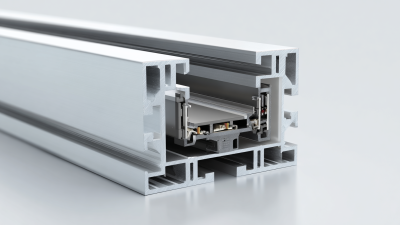
Aluminum profiles are versatile extruded shapes made from aluminum alloy, known for their lightweight yet strong characteristics. These profiles come in various cross-sectional shapes and sizes, allowing them to be tailored for specific applications. The standard production process involves heating aluminum billets until they become pliable, after which they are forced through a die to create the desired profile shape. This process not only optimizes material usage but also allows for the integration of complex designs that can include features such as grooves, channels, and slots.
The unique properties of aluminum profiles contribute to their widespread use across different industries. Their resistance to corrosion makes them ideal for outdoor applications, while their excellent strength-to-weight ratio enables their use in construction, automotive, and aerospace sectors. Additionally, aluminum's recyclability aligns with sustainable practices, further increasing its appeal. From structural frameworks in building designs to components in machinery and transportation, aluminum profiles play a crucial role in enhancing performance and efficiency, showcasing their adaptability to meet the demands of modern manufacturing and design.
The manufacturing process of aluminum profiles is a critical aspect that underpins their application across various industries, such as construction, automotive, and electronics. Initially, the process begins with the selection of high-quality aluminum ingots, which are heated and then extruded through a die to create desired shapes. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global aluminum extrusion market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow significantly due to the increasing demand for lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials in various sectors.
Once extruded, the aluminum profiles undergo several post-processing techniques that enhance their properties and suitability for specific applications. These processes may include anodizing, where a protective oxide layer is created to improve corrosion resistance and surface durability, or powder coating, which provides color and additional protection. The efficiency of these techniques is reflected in industry studies, indicating that proper surface treatment can enhance the longevity of aluminum profiles by up to 50%. As various industries continue to advance in technology, the versatility and strength of aluminum profiles make them an ideal material choice, ensuring ongoing growth and innovation in their manufacturing processes.

Aluminum profiles are increasingly recognized for their versatility and strength in the construction industry. These extruded aluminum sections are used in various applications, from structural components to decorative elements. According to a report by the International Aluminum Institute, the construction sector accounts for nearly 40% of the total aluminum demand globally. This highlights the critical role aluminum profiles play in modern building projects, where efficiency and sustainability are essential.
One of the most common applications of aluminum profiles in construction is in window and door frames. The inherent durability and resistance to corrosion make aluminum an ideal choice for these openings, which need to withstand various environmental conditions. A study by MarketsandMarkets projects that the global aluminum extrusion market in construction will reach USD 69.2 billion by 2025, driven by the rising demand for energy-efficient buildings and sustainable materials. Additionally, aluminum profiles are employed in structural scaffolding, curtain walls, and roof systems, contributing to lighter and more efficient construction processes.
The use of aluminum profiles is also vital in the manufacturing of building facades, offering architects aesthetic flexibility while ensuring structural integrity. This capability is particularly important as the industry moves toward energy-efficient designs. The German Aluminum Association reported that energy-efficient buildings using aluminum systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, aligning with global sustainability goals. Thus, aluminum profiles not only enhance design and functionality but also support the industry's shift toward sustainable construction practices.
Aluminum profiles have become a fundamental component in the transportation sector, particularly in automotive and aviation industries. Due to their lightweight yet sturdy nature, aluminum profiles are increasingly used in manufacturing various vehicle parts. In automobiles, aluminum components help enhance fuel efficiency while providing essential strength and durability. Structural elements such as frames, body panels, and support brackets are often crafted from aluminum, allowing cars to meet stringent performance and safety standards.
In the aviation industry, the application of aluminum profiles is even more critical. The aerospace sector demands materials that not only reduce weight but also offer exceptional resistance to corrosion and fatigue. Aluminum profiles are utilized in the construction of aircraft wings, fuselages, and interiors, facilitating improved aerodynamics and fuel optimization. The inherent properties of aluminum make it an ideal choice for both commercial and military aircraft, supporting innovative designs that contribute to overall efficiency and sustainability in air travel.
Aluminum profiles have emerged as a crucial component in the electronics and consumer goods industries, primarily due to their lightweight nature and excellent thermal management properties. In electronic devices, aluminum profiles serve multiple purposes, from housing enclosures that protect sensitive components to heat sinks that efficiently dissipate heat generated by high-performance processors and power supplies. The ability to be extruded into complex shapes enables designers to create custom solutions that enhance functionality while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
In the realm of consumer goods, aluminum profiles attract attention for their versatility and durability. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing these profiles in everyday products, ranging from furniture to portable gadgets. The combination of modern design and practicality is evident in items like adjustable stands, frames, and protective casings. The use of aluminum not only improves product resilience but also facilitates eco-friendly practices, as it is recyclable and can be produced with reduced environmental impact. By integrating aluminum profiles into their designs, businesses are tapping into a material that supports innovation while addressing consumer demands for sustainability and performance.